Laser Lines are used in various machine vision applications. Examples include laser triangulation, laser light sectioning and many more.
Machine vision applications of Laser Lines
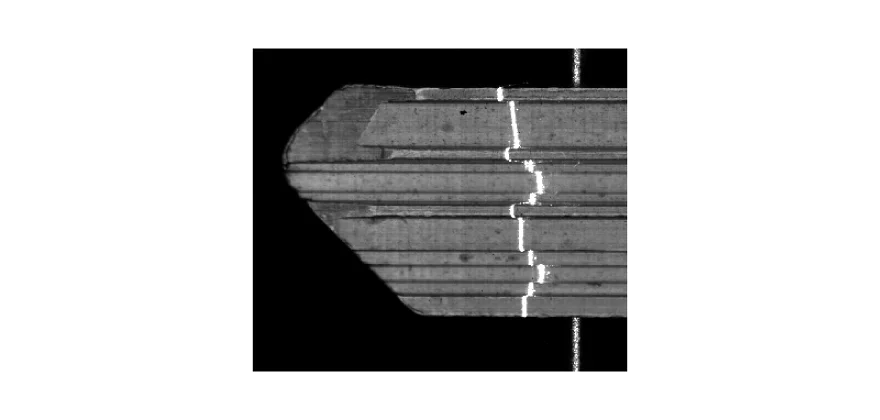
Laser triangulation or Laser light sectioning
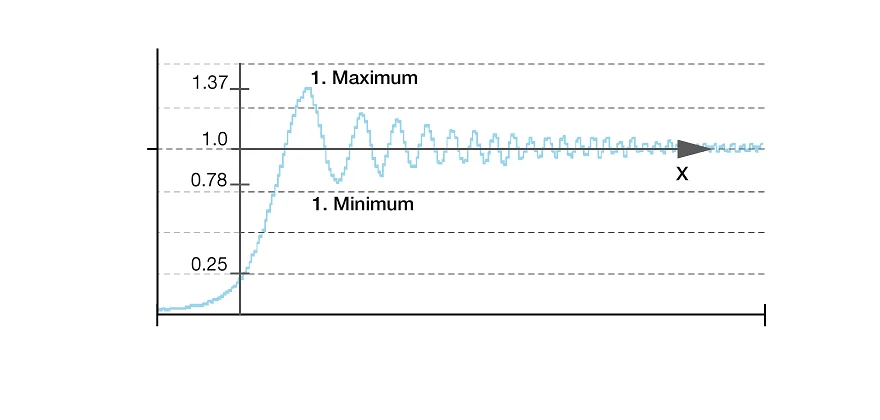
Laser diffraction measurements
One of the most popular applications in laser measurement are laser diffraction measurements. This technique uses telecentric laser beams (that means beams with minimal divergence such as the Laser Diode Collimators Flatbeam®) and can e.g. be used to evaluate the diameter of an object by analyzing the Fresnel diffraction pattern of the shadow edge. [more]
Particle Measurement
Particle counting and measuring is another important application which uses laser lines or laser spots. In the most simple setup a detector registers the light reflected by a particle passing through the laser beam.
Most Laser Line Generators/ Focus Generators are also available as low-noise laser sources series LNC. More details about these lasers can be found here.
Please note: Lasers of series 13LR are not suitable for particle measurements, since the laser line consists of a chain of small dots.
Width and gap measurement
Other applications make use of the smallness of a laser diode emitter. With a typical emitter size of 1 µm x 3 µm, singlemode laser diodes combined with long focal optics result in large laser beams with very small divergence (typical 0.03 mrad). These laser sources are used for width and gap measurements, using simply the shadow, or in more sophisticated cases the diffraction pattern of the object placed into the beam.
Lasers for Machine Vision
Schäfter + Kirchhoff offers various Laser Line Generators, Laser Focus Generators and Laser Diode Collimators for Machine Vision. You can find the adequate laser module here.